ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: Maximizing E-commerce Profit Margins
ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins examines the cost-effectiveness, security, and customer preferences associated with each payment method, offering insights to optimize profitability.
Choosing the right payment processing method is crucial for any US e-commerce business looking to maximize its profit margins. Two of the most common options are Automated Clearing House (ACH) transfers and credit card payments. But which one is better for your bottom line? Let’s dive into a detailed comparison.
This article provides a ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins, exploring the pros and cons of each payment method to help you make informed decisions that can significantly impact your e-commerce success.
Understanding ACH Transfers for E-commerce
Automated Clearing House (ACH) transfers represent a direct bank-to-bank payment method that has steadily grown in popularity within the e-commerce landscape. By sidestepping traditional card networks, ACH offers a different approach to payment processing.
But how exactly do ACH transfers work, and what makes them potentially advantageous for US e-commerce businesses?
The Mechanics of ACH Payments
ACH payments are electronic fund transfers facilitated through the ACH network. This network connects various financial institutions in the United States, enabling the movement of money between bank accounts.
- The customer provides their bank account and routing number to the merchant.
- The merchant initiates a debit request from the customer’s bank account.
- The ACH network processes the transaction, transferring funds from the customer’s bank to the merchant’s bank.
- The transaction typically settles within 1-3 business days.
This direct transfer approach can translate to lower processing fees compared to credit card transactions, a factor that is of high importance in the **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins**.
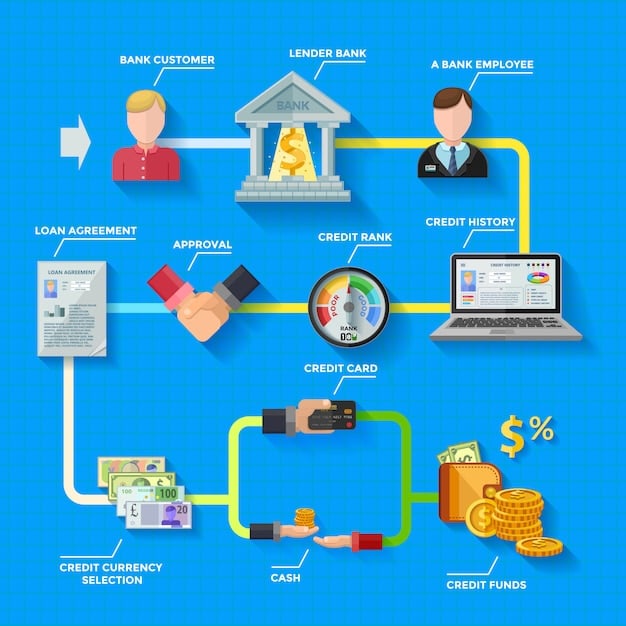
Benefits of Accepting ACH Payments
For US e-commerce businesses, adopting ACH payments can unlock several key advantages. Primarily, the lower transaction fees greatly contribute towards bigger profit margins. Beyond cost savings, ACH payments offer enhanced security protocols to protect against fraud and chargebacks.
- Lower Transaction Fees: ACH typically has lower processing fees than credit cards, which is beneficial for businesses.
- Enhanced Security: ACH benefits from robust security features to protect against fraud and chargebacks.
- Suitable for Recurring Payments: Excellent choice for subscription-based services because of its efficiency.
Understanding these mechanics and benefits provides a solid foundation for comparing **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins**. By understanding this deeply, e-commerce entities in the US can leverage these financial instruments for optimized gains.
Credit Card Payments in US E-commerce
Credit card payments are without a doubt a mainstay of US e-commerce, providing convenience and purchase flexibility to both businesses and patrons. The ubiquitous presence of credit cards in online transactions makes them an unavoidable payment option for e-commerce brands.
Let’s take a closer look at how credit card payments operate within the US e-commerce ecosystem.
How Credit Card Payments Work
When a customer makes a purchase using a credit card online, some processes occur in the background within a matter of seconds. These actions involve multiple parties working together to ensure transactions are securely processed, from authorization to settlement.
- The customer enters their credit card details on the merchant’s website.
- The merchant’s payment gateway encrypts and transmits the data to the payment processor.
- The payment processor routes the transaction to the card network (e.g., Visa, Mastercard).
- The card network verifies the transaction with the issuing bank.
- The issuing bank approves or declines the transaction.
- The payment processor relays the approval or decline back to the merchant.
- If approved, the transaction is settled, and funds are transferred to the merchant’s account.
The speed and ease of credit card payments have made them an integral part of the online shopping experience, though, the costs associated must be considered when viewing **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins**.
Advantages of Accepting Credit Card Payments
While credit card processing fees can be higher than those of ACH, accepting credit cards offers distinct benefits for e-commerce merchants. Foremost are the broad customer acceptance and the likelihood of boosted sales thanks to the ease of credit availability.
- Broad Customer Acceptance: A lot more customers are likely to have credit cards rather than using ACH, thus offering this option attracts a wider range of potential sales.
- Purchase Flexibility: Credit cards allow customers to make purchases even when they don’t have sufficient funds in their bank accounts.
- Increased Sales Potential: Credit card acceptance can lead to increased sales.
Understanding the mechanics and benefits of credit card payments is crucial for US e-commerce businesses to make sound decisions when performing an **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins**. Both payment options bring unique capabilities in the ever-evolving landscape of digital sales.
Cost Comparison: ACH vs. Credit Card Payments
One of the most important factors for e-commerce businesses when deciding on payment methods is cost. Let’s break down the cost structures of both ACH and credit cards highlighting their respective advantages when weighing **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins**.
A detailed cost analysis can help e-commerce businesses determine which payment method aligns best with their financial goals.
Transaction Fees
Transaction fees are the fees charged by payment processors for each transaction. These fees can vary depending on the payment method and the payment processor.
- ACH: Usually involves lower transaction fees than those applied to credit card payments. ACH charges often involve a flat fee per transaction or a percentage-based fee with a cap.
- Credit Cards: Composed of interchange fees set by card networks, assessment fees collected by card issuers, and a markup charged by the payment processor.
The difference in transaction fees can be considerable, especially for high-volume e-commerce businesses. The lower expenses for those who select **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins** create a tempting route to increase profits by decreasing expenses.
Other Costs to Consider
Beyond transaction fees, there are other costs to consider when evaluating these different payment options. These additional costs can include setup fees, monthly fees, and chargeback fees.
- Setup Fees: Some payment processors charge setup fees for integrating ACH or credit card payments into an e-commerce platform.
- Monthly Fees: Certain payment processors might impose monthly fees for utilizing their services.
- Chargeback Fees: Chargeback fees are assessed when a customer disputes a transaction, resulting in a reversal of funds.
When assessing **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins** it’s best to account for all potential expenses involved, offering a comprehensive basis for choosing processing methods.

Security and Risk Management
When choosing how to process your payments some of the very important factors to consider are the security and the risk management involved. Let’s take a deeper look into the characteristics of credit cards and ACH transfers.
Understanding these distinctions is essential for e-commerce businesses striving to create a secure payment environment, particularly when considering **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins**.
Fraud Prevention Measures
E-commerce businesses must implement strong fraud prevention measures to protect themselves and their customers from fraudulent transactions. These measures can include address verification, card verification values, and fraud monitoring systems.
- ACH: ACH transactions benefit from security features like account verification, risk monitoring, and fraud detection tools.
- Credit Cards: Employs fraud prevention tools such as address verification systems (AVS), card verification values (CVV), and 3D Secure authentication.
Businesses want to optimize for financial gain by leveraging the attributes of either **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins** while maintaining defenses to maximize profit and security.
Chargeback Rates and Disputes
Chargebacks—return of money to a consumer after a disputed transaction—are a considerable risk for e-commerce businesses. Disputes can occur for various reasons, including fraud, unauthorized transactions, or dissatisfaction with the goods or services received.
- ACH: Generally experiences lower chargeback rates than credit card payments. ACH disputes typically arise from unauthorized transactions or errors in processing, with resolution being direct since they’re bank-to-bank.
- Credit Cards: Businesses accepting credit cards face higher rates of chargebacks because of fraud or customer dissatisfaction.
As businesses carefully consider **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins**, being careful with security is essential for increasing customer confidence and mitigating costs.
Data-Driven Decision Making
To make informed decisions about payment methods, e-commerce businesses should leverage data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior and payment preferences. Analysing data can lead to improved processes, higher profits, and happier customers.
Here’s how data-driven insights may enhance strategic planning by looking at **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins**.
Analyzing Customer Payment Preferences
Understanding how your customers prefer to pay is crucial for optimizing your payment options. It allows you to tailor the payment experience to match their expectations while also catering to those who might be on the fence when it comes to completing a purchase online.
- Transaction Data: Businesses can identify any transaction patterns by evaluating payment method trends related to demographic and geographic customer data.
- Surveys and Feedback: Collect direct insights from customers to learn about their payment preferences.
These data enable businesses to align their payment options to increase customer pleasure and sales conversion percentages while considering **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins**.
Optimizing for Profit Margins
By tracking key metrics such as transaction fees, chargeback rates, and conversion rates, e-commerce businesses can optimize their payment strategies to profitability. This is particularly important, regardless of whether you pick ACH transfers or credit card payments.
- A/B Testing: Experiment with different payment setups to see how they affect crucial KPIs such as conversion rates and revenue per transaction.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Compare the expenses involved with each means of payment, including costs for processing, chargebacks, and fraud prevention against increased sales potential.
Adopting data-driven approach allows e-commerce companies to fine-tune their payment systems and maximize cost effectiveness. Thorough insight into **ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins** provides actionable recommendations for optimization.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 💰 Lower Fees (ACH) | ACH often has lower processing costs than credit cards. |
| 💳 Wide Acceptance (Credit Cards) | Credit cards are more widely used by consumers. |
| 🛡️ Security Measures | Both methods have security to protect against fraud. |
Frequently Asked Questions
ACH payments are direct bank transfers with lower fees but slower processing times. Credit card payments offer instant transactions and broader customer acceptance at higher costs.
ACH transaction fees are typically lower, often a flat fee or a small percentage, while credit card fees include interchange, assessment, and processor markups that are usually higher.
Both payment methods have security measures. ACH benefits from account verification, while credit cards use AVS, CVV, and 3D Secure. ACH payments generally have reduced chargeback rates.
Businesses should assess transaction fees, chargeback rates, customer payment preferences, security needs, and data analysis to optimize payment strategies for profitability.
Data analysis provides insights into customer behaviour and payment preferences, enabling businesses to optimize their payment options, track key metrics, and optimize for efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the nuances within ACH vs. Credit Card Payments: A Data-Driven Analysis for US E-commerce to Maximize Profit Margins is essential for US e-commerce businesses. Weighing transaction costs, security issues, and user preferences will help companies optimize their payment procedures.
Adopting those findings and insights empowers e-commerce companies to fine-tune payment systems that enhance shopper experience, strengthen security against fraud, and optimize profit margins. The e-commerce market in the US will be won through smart decisions and by knowing precisely what your customers need.





